Singapore Employee Rights Guide (2024): Compassionate Leave in Singapore, Overtime & More
 Ruth Lum
Ruth Lum●
When you encounter a “Terms and Conditions” page, do you read every word?
Or do you just scroll straight to the bottom and click on the “I Agree” button?

Guilty of the latter?
Yep, me too.
When it comes to a job, it’s even MORE important to take a good, detailed look at what’s in it for you before you sign the contract.
If you’re still looking for a job, you can use this guide to help you find out what employee benefits and entitlements you’re supposed to get!
And if you’ve already signed a contract without looking at the terms and conditions…
Well, you might want to find out if you’ve been short-changed.
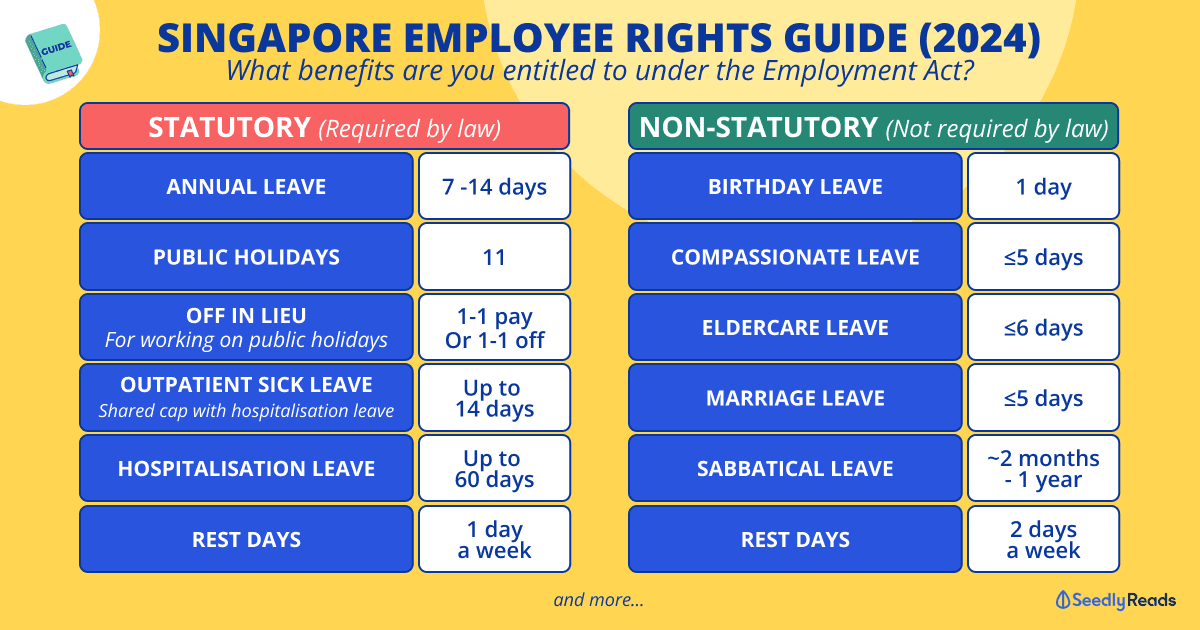
TL;DR: What Kind Of Employee Benefits Am I Entitled To?
Assuming you are a Singapore citizen and have worked for at least three months with your employer.
Here’s what you’ll get:
| Ministry of Manpower Guidelines | Market Rate | Can Carry Forward to Next Year? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Statutory (Legally Required) | |||
| Annual Leave | 7 - 14 days (Depending on length of service) | ~14 to 30 days | Yes |
| Public Holidays | 11 days | 11 days | No |
| Off-In-Lieu (For working on Public Holidays) | One to one day (If you work on a public holiday, by default, your employer should pay you an additional day's pay. OR A public holiday in lieu or Time off in lieu in return) | One to one day (If you work on a public holiday, by default, your employer should pay you an additional day's pay. OR A public holiday in lieu or Time off in lieu in return) | No |
| Rest Day(s) | One rest day a week (Maximum interval allowed between 2 rest days is 12 days) | Two rest days | No |
| Outpatient Sick Leave (Shared cap with hospitalisation leave) | Up to 14 days | Up to 14 days | No |
| Hospitalisation Leave | Up to 60 days | Up to 60 days | No |
| Childcare Leave (Separate cap for both parents) | Up to 6 days | Up to 6 days | No |
| Maternity Leave | Up to 16 weeks | Up to 16 weeks | No |
| Paternity Leave | 2 - 4 weeks | 2 weeks | No |
| Shared Parental Leave (From Maternity Leave entitlement) | 4 weeks (Subject to wife's agreement) | 4 weeks (subject to wife's agreement) | No |
| Adoption Leave | 12 weeks | 12 weeks | No |
| Non-Statutory (No Legal Requirement) | |||
| Birthday Leave | — | 1 | No |
| Compassionate Leave | ≤5 days | No | |
| Eldercare Leave | ≤6 days | No | |
| Marriage Leave | ≤5 days | No | |
| Sabbaticals | ~2 months to 1 year | No | |
For more information, you can refer to the Ministry of Manpower’s Employment Act!
Click to Teleport
- What Is The Employment Act?
- Singapore Employment Act Changes Explained
- What Statutory Leaves Am I Entitled to as an Employee?
- What Kind of Non-Statutory Leaves and Benefits Are There?
- Other Non-Statutory Employee Benefits & Perks That You Might Be Able to Enjoy
What Is The Employment Act?

The Employment Act is Singapore’s main labour law.
It covers the basic terms and working conditions for all types of employees — with some exceptions.
Note: exceptions include seafarers, domestic workers, and public officers who are covered by other Acts and regulations due to the nature of their work
It’s an everchanging and evolving legal document that is often amended to protect the interests of both the employers as well as the employed.
Singapore Employment Act Changes Explained

Here are the changes that take effect from 1 April 2019.
Covering All Employees Under The Employment Act: MOM Annual Leave Guidelines and More
Managers and executives with a monthly basic salary of more than $4,500 will be covered by the Employment Act.
This amendment effectively covers all employees in Singapore with regard to:
- Minimum days of annual leave
- Paid public holidays and sick leave
- Timely payment of salary
- Statutory protection against wrongful dismissal.
Note: exceptions include those mentioned earlier who are covered by other Acts and regulations.
Covering More Non-Workmen Under Part IV of The Employment Act
This amendment includes non-workmen who earn up to $2,600 under Part IV of the Employment Act.
Part IV of the Employment Act provides additional protection such as:
- hours of work
- rest
- overtime pay.
Wrongful Dismissal Claims to be Heard by Employment Claims Tribunal (ECT)
As the ECT already hears salary-related claims, the shift will provide a more convenient one-stop service for employees and employers.
This should hopefully improve the employment dispute resolution framework.
What Statutory Leaves Am I Entitled to as an Employee?
If you’re a
- full-time
- part-time
- temporary, or
- contract
employee, here are some of the more common benefits which you are entitled to by law.
FYI: “statutory” means relating to rules or laws, which have been formally written down. So, legally, you’re entitled to these benefits.
Minimum Annual Leave Singapore: 21 Days Annual Leave in Singapore?

Although the MOM stipulated requirement is a minimum of seven days of annual leave.
It’s a common practice in Singapore to grant employees a minimum of 14 days of annual leave.
In addition, an additional one day of annual leave will be given for every additional year that you are with the company:
| Year of Service | Days of Leave |
| 1st | 7 |
| 2nd | 8 |
| 3rd | 9 |
| 4th | 10 |
| 5th | 11 |
| 6th | 12 |
| 7th | 13 |
| 8th and thereafter | 14 |
Based on what my friends in other companies and industries have shared, the most generous of companies (usually Multi National Companies) often grant up to 30 days of annual leave!
There are even reports of companies that offer unlimited paid leave. But taking it all is a story for another day.
For special situations like:
- unconsumed annual leave
- unpaid or no-pay leave
- taking leave on a workday when a half-day off is given
you’ll have to check with your employer or Human Resources (HR).
Side note: if you plan your leave to coincide with certain long weekends in 2024, did you know that you can disappear from work for 27 days:
Public Holiday Singapore (2024)

You are entitled to 11 paid public holidays a year.
In case you aren’t aware (how can it be…), there are a total of 11 gazetted public holidays for 2024:
| Date | Day | Holiday image | Holiday name |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Jan 2024 | Monday |  |
New Year’s Day |
| 10 Feb 2024 11 Feb 2024 |
Saturday Sunday |
 |
Chinese New Year
Monday, 12 Feb 2024, will be a public holiday. |
| 29 Mar 2024 | Friday |  |
Good Friday |
| 10 Apr 2024 | Wednesday |  |
Hari Raya Puasa |
| 1 May 2024 | Wednesday |  |
Labour Day |
| 22 May 2024 | Wednesday |  |
Vesak Day |
| 17 Jun 2024 | Monday |  |
Hari Raya Haji |
| 9 Aug 2024 | Friday |  |
National Day |
| 31 Oct 2024 | Thursday |  |
Deepavali |
| 25 Dec 2024 | Wednesday |  |
Christmas Day |
Source: MOM
Note: If the holiday falls on a rest day (Saturday or Sunday), the next working day will be a paid holiday.
MOM Off-In-Lieu Singapore
If you’re required to work during a public holiday, MOM requires that your Singapore-based employer should pay you an extra day’s salary OR grant you a day off-in-lieu.
What is Off in Lieu: Holiday in Lieu Meaning
In case you’re wondering, “in lieu of” means to “replace or substitute for”.
Apart from earning an off-in-lieu when you work on a public holiday, there are also other situations where you might be given an off-in-lieu.
This really depends on your company.
Some practice a one-to-one compensation for the number of days you worked in excess.
This means that if you have to attend a work-related event on a Saturday (non-working day), you should get a one-day off-in-lieu.
Outpatient Sick Leave Singapore

The MOM stipulated requirement is up to 14 days of paid sick leave in a year based on how long you have been working for the company.
To be eligible for sick leave, you must:
- Be covered under the Employment Act
- Have served your employer for at least three months
- You have informed or tried to inform your employer within 48 hours of your absence
- You should submit your medical certificate as soon as you return to work.
On top of that, you must produce a medical certificate and be certified to be unfit for work by a registered medical practitioner registered under the Medical Registration Act or Dental Registration Act. In other words, qualified doctors and dentists.
In addition, if you’ve been employed for a duration of at least six months, you’ll be eligible for the complete sick leave entitlement.
But if you only joined the company recently, your paid sick leave is calculated based on how long you’ve been with the company. Your service period starts on the day you commence employment. To qualify for paid outpatient or hospitalization leave, you must have a minimum of three months of employment. If your tenure falls between three and six months, your entitlement will be prorated. Here is an example of how it works for an employee who starts work on 13 February 2023:
| Number of Months of Service Completed | Entitled to Paid Sick Leave on | Paid Outpatient Sick Leave (days) | Paid Hospitalisation Leave (days) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 13 May | 5 | 15 |
| 4 | 13 June | 8 | 30 |
| 5 | 13 July | 11 | 45 |
| 6 and thereafter | 13 August | 14 | 60 |
In the example shown above, any sick leave taken between 13 Feburary to 12 May 2023 will be unpaid.
Moreover, paid sick leave days are subject to specific limits. Your allowance for paid outpatient sick leave and paid hospitalisation leave cannot exceed your sick leave entitlement. Let’s say you have already utilized 14 days of paid outpatient sick leave within a year; your remaining allocation for paid hospitalisation leave would be 46 days (60 – 14 = 46).
Hospitalisation Leave Singapore

The MOM stipulated requirement is 60 days of paid hospitalisation leave in a year. As mentioned above, the 14 days of paid outpatient sick leave falls under this cap.
Paid hospitalisation leave is designed to cater to situations where a hospital doctor determines that an employee needs hospital care. This includes instances when the employee is admitted to the hospital, undergoes day surgery, experiences non-hospitalized conditions that necessitate bed rest (such as pregnancy-related complications), or requires additional recuperation and medical attention following discharge from the hospital for their ailment.
To be eligible to take paid hospitalisation leave:
- You must be covered under the Employment Act
- You must have served your employer for at least 3 months
- You should have informed or tried to inform your employer within 48 hours of your absence.
To y for paid hospitalisation leave, you must:
- Warded in a hospital as an in-patient or for day surgery
- Quarantined under any written law
- Certified by a medical practitioner who can admit patients into an approved hospital, including medical practitioners from national speciality centres and ambulatory surgical centres.
Do not that Paid hospitalisation leave is not considered an extension of paid outpatient sick leave.
Also, employers have no obligation to provide paid sick leave or cover medical consultation fees for cosmetic procedures. The determination of whether a procedure is cosmetic or not lies with the attending medical practitioner. However, your company’s policy may include this as part of its employee medical benefits.
Childcare Leave Singapore

Each parent is entitled to up to six days of childcare leave per year until the year your child turns 7 years old.
The amount of leave childcare leave you have depends on the fulfilment of these criteria:
- My child is a Singapore citizen.
- My youngest child is below seven years old.
- I have worked for my employer or have been self-employed for at least three continuous months.
Childcare leave is capped at 42 days for each parent.
Your yearly childcare leave entitlement must be consumed by the end of that year.
In terms of payment, the following parties are responsible:
- The first three days will be paid by your employer.
- The remaining three days will be paid for by the Government.
- Payments are capped at $500 per day, including CPF contributions.
One more thing.
Childcare leave typically follows the default calendar year, spanning from January 1st to December 31st. Nevertheless, you can actually arrange with your employer to adopt an alternative 12-month period, such as your financial year or work anniversary, for this purpose.
Maternity Leave Singapore

| No of Days (MOM guidelines) | No. of Days (Set by some companies) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Maternity Leave / Adoption Leave | Child is a citizen: 16 weeks Child is a non-citizen: 12 weeks (8 weeks paid, 4 weeks unpaid) | Child is a non-citizen: 12 weeks paid |
| Shared Parental Leave | Husband can apply for 4 weeks of wife's 16 weeks | N/A |
| Unpaid Infant Care Leave For Singapore citizen under 2 years of age. You will also need to be be employed for at least 3 months | 6 | 6 |
| Child Care Leave For children under 7 years old | 6 | 6 |
As a working mother, you are entitled to 16 weeks of Government-Paid Maternity Leave if:
- Your child is a Singapore citizen
- For employees: you have served your employer for at least three months before the birth of your child
- You have given your employer at least one week’s notice before going on maternity
- For self-employed: you have been engaged in your work for at least three months and have lost income during the maternity leave period
If your child is not a Singapore citizen:
- You are only entitled to 12 weeks of maternity leave.
- On top of that, your employer will pay your usual monthly salary for the first eight weeks of leave.
- And the last four weeks of maternity leave will be unpaid (subjected to the terms you agreed with your company).
If you have not worked for your employer for at least three consecutive months, you can still take 12 weeks of unpaid maternity leave.
Unwed mothers are also entitled to maternity leave.
- 16 weeks of Government-Paid Maternity Leave or
- 12 weeks of maternity leave, depending on whether your child is a Singapore citizen and other criteria here.
During your leave, your employer will pay your salary. Subsequently, they can seek reimbursement from the Government as per the guidelines of the Government-Paid Maternity Leave (GPML) scheme:
| Births | Paid by employer | Reimbursed by Government |
| First and second | First 8 weeks, at your gross rate of pay | Last 8 weeks, capped at $10,000 per 4 weeks or a total of $20,000 |
| Third and subsequent | – | All 16 weeks, capped at $10,000 per 4 weeks or a total of $40,000 |
Paternity Leave Singapore

| No of Days (M.O.M guidelines) | No. of Days (Set by some companies) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Paternity Leave / Adoption Leave | 10 days | 10 days |
| Shared Parental Leave | Up to 4 weeks of wife's 16 weeks | N/A |
| Unpaid Infant Care Leave | 6 | 6 |
| Child Care Leave (for children under 7 years old) | 6 | 6 |
As a working father, you are entitled to up to four weeks of Government-Paid Paternity Leave (GPPL) if:
- Your child is a Singapore citizen
- You have been lawfully married to the child’s mother between conception and birth
- For employees: you have served your employer for at least three months before the birth of your child
- For self-employed: you have been engaged in your work for at least three months and have lost income during the paternity leave period (self-employed).
Moreover, adoptive fathers who fulfill the specified criteria are also eligible for GPPL for any childbirth:
- Your child is a Singapore citizen
- For employees: you have served your employer for a continuous period of at least three months before the date of your formal intent to adopt
- For self-employed: you have been engaged in your work for a continuous period of at least three months before the date of your formal intent to adopt and have lost income during the paternity leave period.
Each week of GPPL, including CPF contributions, has a maximum limit of $2,500.
Starting from 1 January 2024, GPPL will be doubled from two to four weeks for fathers of children who are born from 1 January 2024. Employers have the option to provide the extra two weeks of GPPL voluntarily, and the government will reimburse them.
You can use your leave in the following manner:
| Arrangement | 2 weeks GPPL |
|---|---|
| Default, without any mutual agreement | Take 2 continuous weeks within 16 weeks after the birth of the child. |
| Flexible, by mutual agreement | Take 2 continuous weeks any time within 12 months after the birth of the child.
Split the 2 weeks into working days and take them in any combination within 12 months after the birth of the child. |
| Calculating actual leave days | 2 weeks X the number of working days in the week.
Capped at 6 working days per week. |
Adoption Leave Singapore

Eligible adoptive mothers (including those who are self-employed) are entitled to 12 weeks of paid adoption leave.
You’ll have to take the leave in one stretch or as agreed with your employer.
You are eligible for adoption leave if:
- Your adopted child is below the age of 12 months at the point of your formal intent to adopt. “Formal intent to adopt” is defined as:
- For a local child: when you file the court application to adopt.
- For a foreign child: when in-principle approval is granted for a Dependant’s Pass.
- Your adopted child is a Singapore citizen
- Your child is a foreigner:
- One of the adoptive parents must be a Singapore citizen
- the child must become a Singapore citizen within six months of adoption
- You have served your employer or been self-employed for at least three months before your formal intent to adopt
- The adoption order must be passed within one year of your formal intent to adopt.
The reimbursement is capped at a maximum of $20,000 for the first and second children and $30,000 for the third child onwards, which includes CPF contributions.
Working Overtime in Singapore

For employees covered under Part IV of the Employment Act, your contractual hours of work for common work arrangements are:
| If you work | Your contractual work hours are |
|---|---|
| 5 days or less (a week) | Up to 9 hours/day OR 44 hours/week |
| > 5 days (a week) | Up to 8 hours/day OR 44 hours/week |
| Less than 44 hours every alternate week | Up to 48 hours a week, but capped at 88 hours in any continuous 2-week period. Example: If week 1 = 40 hours; week 2 = 48 hours; week 3 = 40 hours: Average for weeks 1 and 2 = 44 hours Average for weeks 2 and 3 = 44 hours |
| Shifts of up to 12 hours a day | Up to an average of 44 hours over a continuous 3-week period. Example: If week 1 = 40 hours; week 2 = 44 hours; week 3 = 48 hours; week 4 = 40 hours: Average for weeks 1, 2 and 3 = 44 hours Average for weeks 2, 3 and 4 = 44 hours |
Note that if you are not classified as a shift worker, you can still work up to 12 hours per day, with the condition that the average does not exceed 44 hours over any consecutive three-week period, you are required to:
But you will need to:
- Give your consent in writing.
- Have the provisions of Sections 38 and 40 of the Employment Act explained to you.
- Be informed of your daily working hours, number of working days in each week and weekly rest day.
Overtime Pay Singapore
Overtime work refers to any work performed beyond the regular working hours, excluding breaks.
You are eligible to claim overtime if you meet one of the following criteria:
- You are a non-workman earning a monthly basic salary of $2,600 or less.
- You are a workman earning a monthly basic salary of $4,500 or less. In general, a workman typically engages in manual labour, so you should determine if your job falls into this category.
The maximum overtime rate for non-workmen is limited to either the salary threshold of $2,600 or an hourly rate of $13.60.
Ensure you receive your accurate overtime payment promptly. Any work performed beyond the contracted hours is classified as overtime hours.
For overtime work, your employer is required to compensate you at a rate of at least 1.5 times your regular hourly base pay. This payment should be made within 14 days following the conclusion of the salary period.
What are the Maximum Hours of Overtime I Should Clock?
As an employee, you are not allowed to work more than 12 hours a day.
HOWEVER.
Your employer can ask you to work for more than 12 hours a day and not exceeding an average of 44 hours over any three continuous if there are:
- An accident or threat of an accident
- Work that is essential to the life of the community, national defence or security
- Urgent work to be done to machinery or plant
- Interruption of work that was impossible to foresee.
This will also need to apply for an overtime exemption.
An employee can only work up to 72 overtime hours in a month.
However, employers can apply for an exemption if they require employees to work for more than 72 hours of overtime in a month.
Work performed on rest days or public holidays is not considered part of the 72-hour overtime limit, except for any additional hours worked beyond the standard daily working hours on those specific days. These additional hours are factored into the 72-hour limit.
The computation for overtime on a rest day or public holiday is as follows:
(Hourly basic rate of pay × 1.5 × Number of overtime hours worked) + (Payment for rest day or public holiday)
Rest Days Singapore
Your employer is obligated to grant you one day off per week.
A full rest day spans from midnight to midnight and is not a paid day.
For shift workers, the rest day can be a continuous block of 30 hours. A 30-hour rest period that commences before 6pm on a Sunday is considered a single rest day for the week, even if it extends into the following Monday.
A week is defined as a continuous 7-day period that begins on Monday and ends on Sunday.
Your employer cannot require you to work on your designated rest day unless there are exceptional circumstances.
Regarding when the rest day can occur, your employer has the authority to choose any day of the week as the rest day, which can include Sunday.
Aside from the rest day, the other days of the week during which you are not required to work are not classified as rest days.
If the rest day falls on a day other than Sunday, your employer should create a monthly schedule and inform you about the rest days in advance of each month.
The maximum gap between two consecutive rest days allowed is 12 days.
Most compaines in Singapore offer two rest days on Saturday and Sunday.
What Kind of Non-Statutory Leaves and Benefits Are There?
Most companies in Singapore provide certain non-statutory leaves and benefits to their employees. Take note that there is no statutory entitlement for the leaves mentioned below. In other words there is no legal requirement for these leaves.
These are dependent on your employment contract (that’s why you need to read it carefully!).
Or on mutual agreement between you and your employer.
Often, these are included for the welfare of a company’s employees.
As a potential employee of a company, some of these benefits are potential game-changers as they are a good indication of how much a company values and wants to retain talent.
Compassionate Leave MOM Regulations
As mentioned above, companies are not legally required to provide these benefits. But, these benefits, like compassionate leave and marriage leave, also indicate how progressive a company is.
Birthday Leave Singapore

It’s exactly what it means.
You’ll get one day of paid leave, which you can use to celebrate your birthday.
I mean, c’mon.
Who would want to work on their birthday?
Compassionate Leave Singapore / Bereavement Leave Singapore / Condolence Leave

Compassionate leave is paid leave that allows you to attend or prepare a funeral for deceased family members.
As a rule of thumb, companies usually offer at least two to three days of paid compassionate leave.
But I’ve heard of companies who give at least five days.
This should be clearly stated in your employment contract.
If it isn’t, fret not.
Employers will usually grant compassionate leave when you inform them about a death in the family.
However, this is usually only granted for deaths within your immediate family and might not be applicable to more distant relatives.
Compassionate Leave for Immediate Family = Compassionate Leave for Grandparents, Parents, Siblings and More
This means that only the death of:
- grandparents
- parents
- siblings
- in-laws
- children, and
- grandchildren.
are applicable for compassionate leave.
Eldercare Leave Singapore

This is paid leave for you to take time off to take care of your elderly parents or family members when they are ill.
Unfortunately, the government is still studying the idea of eldercare leave in consultation with tripartite partners.
Companies with family-friendly policies will usually give between four to six days of eldercare leave.
MOM Marriage Leave Singapore: Singapore Marriage Leave Explained

As most couples have their weddings on a weekend, this is paid leave for you to plan or get ready for your big day!
Most companies will give two to three days of marriage leave. But, do note that it is not legally required by MOM.
Sabbaticals Singapore
This is probably the most subjective — and rarest — of all the non-statutory leaves which a company can grant an employee.
A sabbatical is a period away from work that is mutually agreed upon between you and your employer.
Think of it as a ‘gap year’ or an extended break from work before you come back to the same job.
Note: considering that you’re paid and you’ll be taking an extended period of absence, sabbaticals are usually only granted (on a case-by-case basis) to senior employees who have worked and contributed to the company for a long period of time.
Depending on your company’s policies, some will pay your base salary for the entire period of the sabbatical.
While some will pay 40% of your pre-sabbatical base salary until you return to your job.
How long you can spend away will really depend on how critical your role is and how long your employer can afford to have you away for.
And this could be anything between two months to a year.
Other Non-Statutory Employee Benefits & Perks That You Might Be Able to Enjoy
Beyond off days and leaves, some other common employee benefits include:
Healthcare, Well-Being and Personal Benefits
Many Singapore companies offer medical insurance plans that extend to your dependents and typically cover personal accidents and hospitalisation.
Per Diem Allowance
For travel-related jobs, many companies provide a per-day:
- allowance
- transportation allowance, or
- reimbursement of all expenses incurred while travelling on the job.
The per diem amount depends on the place you have to travel to for work.
Relocation Package
Most companies provide a relocation allowance to employees who have to move to another country.
Often, these packages include benefits for the employer’s family if they need to uproot them as well.
Stock Options
Some companies give employers a chance to own a stake in the company.
This is usually offered through company stock options and is usually given to senior employees.
Other Common Perks
Other perks include:
- Organised sports and activities
- Paid corporate memberships
- Paid or subsidised mobile phone plans
- Paid or subsidised gym and club memberships
- Sponsored employee training, upgrade, or educational courses
- Staff referral schemes
- Monthly or annual team outings (fully paid) for team-bonding
and many more…
Singapore Employee Rights
If you feel that you’re being shortchanged, talk to your employer or HR department to seek redress.
If your company or employer has violated your rights as dictated in the Employment Act…
You can report an Employment Act violation with regard to matters like:
- Salary
- Annual Leave and Sick Leave
- Public holidays entitlement
- Hours of work, overtime, and rest days
You’ll need:
- A valid SingPass
- Details of your employer, e.g. company name, Unique Entity Number (UEN)
- Your personal particulars, e.g. address, NRIC, contact number
- Your employment details, e.g. start and end date of employment, occupation, salary
You might also need to provide supporting documents like:
- Employment contract
- Payslips
- CPF statement or bank statement
- Resignation or termination letter
- Timesheets or punch card
- Medical certificate or medical bill
Alternatively, you can:
- Call MOM’s Workright hotline: 1800 221 9922
- Monday to Friday: 8.30am to 5.30pm
- Saturday: 8.30am to 1pm
- Closed on Sundays and public holidays
- Or email: [email protected]
Don’t worry; your identity will be kept strictly confidential!
Read More
- Singapore Public Holidays 2024 & Long Weekend Guide: Take 6 Days of Leave for 27 Days off Work!
- Mental Health Leave in Singapore: This Company Gives Employees up to 6 Months Leave To Recover From Their Mental Health Ailments
- More Baby Bonus & Paternity Leaves: Did Budget 2023 Address Young Parents’ Concerns?
Advertisement